ADHESO Gripper that adapts according to the workpiece
When handling objects, it comes with various dimensions, structures, and materials that demand different end-effectors to collect. With this new technology, robots can grasp the object so long it is within the range of the robot’s payload.
Author: Ho Xiu Ting  Date: 10th August 2021
Date: 10th August 2021
![]()
![]()
No matter what shape or material the robot is handling, engineers/ manufacturers have to produce another set of grippers to fit the criteria of the new item the robot is picking. What if there is a product that can adapt to various surfaces and workpieces? Engineers can make use of this product to grasp perfectly different ranges of applications.
Adhesive gripping technology from SCHUNK applied the principle of adhesion and uses intermodular acting Van der Waals forces to handle different workpieces. The fact that ADHESO gripper is using Van Der Waals to pick and place the object, it does not require additional energy to be supplied to the end-effector. It removes additional components like cables for electricity, pumps for vacuum or suction and etc.
ADHESO Technology
Van der Waals force is a distance-dependent interaction between atoms, and it vanishes when the distance between the interacting molecules is further. It includes attraction and repulsion between atoms, surfaces, and other intermolecular forces. Although Van der Waals force has the weakest bond among the other bonding, it can still support integral structure load.
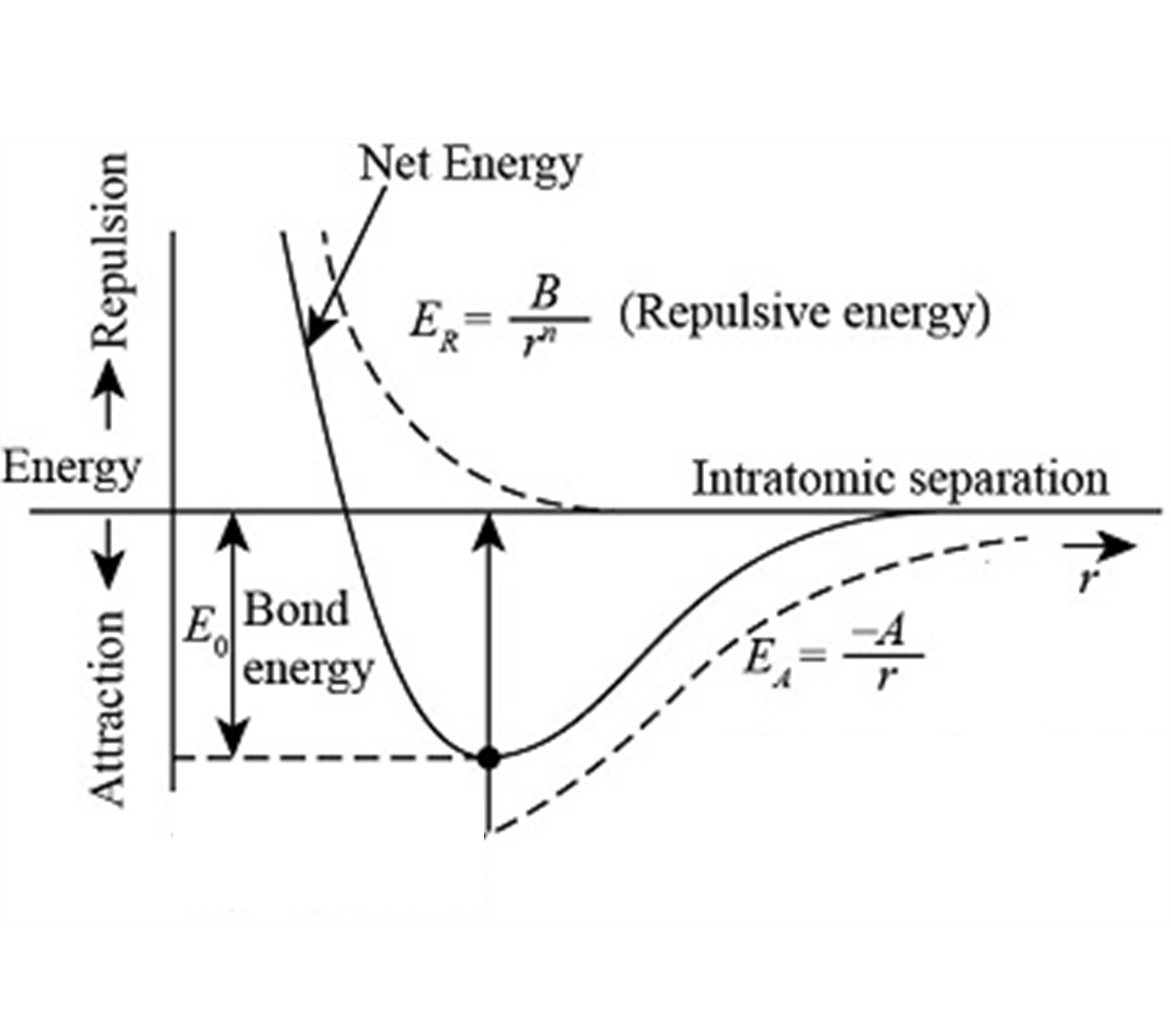
To separate 2 atoms that are bonded together, it has to overcome the bonding energy.
Hence, the bonding energy is negative as the robot has to supply repulsive energy for them to separate. This allows the atoms to wander freely again until the next bonding occurs.
A charged body (ADHESO Gripper) attracts other bodies irrespective of whether they are insulators or conductors.

The particles in the workpiece are re-arranged in order to form the bonding between the workpiece and the ADHESO gripper. This results in molecules that are subjected to forces to bring particles nearer together and bring them into a stronger field.
Releasing Mechanism
When attaching ADHESO gripper to Meca500, it can grip components using the Van Der Waals technology. When the gripper releases the component after reaching its designated position, it will have to break the bond between the objects. For that to happen, Meca500 can separate by 3 different releasing mechanisms shown below.
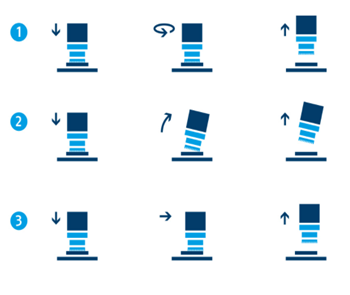
1. Controlling Joint 6 of Meca500 to rotate on the spot to break the bond between the ADHESO gripper and the workpiece.
2. Direct Meca500 to angle its fifth joint to create a repulsive force against the ADHESO gripper.
3. Command Meca500 to slide against the workpiece to create friction force against ADHESO gripper.
Applications
IC Chip
ADHESO Gripper is made from special polymers that have a unique surface architecture to pick up various objects with different surfaces.

Electronics components like IC chips can be transferred from one breadboard to another using the ADHESO gripper.
As each hole in the breadboard is drilled, the drill portion wears down a little, hence, causing the tolerance of the hole to oversize slightly. Especially when the IC chip has 32 legs, making the accuracy and repeatability to be extremely important when the transfer is made.
Click here to view the full procedure of Meca500 collecting the IC chip from the rack using its 5 μm position repeatability to place it on the breadboard. This can help to check if the pins are straight before sending the chip out of the manufacturing company.
Wafer
It can also be integrated into the semiconductor industry to pick and place the wafer into the machine to carry out a process. When it grips on the object, it leaves no residue so as to protect the wafer from being contaminated.

Click here to understand the full process of Meca500 transferring wafers from a location to Front Opening Unified Pod (FOUP) for the further process to be done in the cleanroom. In order to separate the wafer from the gripper, Meca500 has to tilt its fifth joint to simulate this motion. As the ADHESO gripper is particle-free, it does not leave any residue on the surface.
Disc

Click here to observe how the discs are being stacked from one position to another without leaving any blemishes on the surface. In manufacturing, it is important to stack a layer of protectors to prevent any damage caused during transportation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we can see that ADHESO gripper using Van Der Waals technology can come together to perform various applications using Meca500. Its versatility in use and ideally adaption to different ranges of functions will be beneficial to clients with different needs. Feel free to contact us if you wish to see a demonstration and stay tuned for more application videos in the future.
Reference
1. Adair, J. H., Suvaci, E., & Sindel, J. (2003, January 1). Surface and colloid chemistry. Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology (Second Edition). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B0080431526016223?via%3Dihub. 2. ADHESO. (2021, July 7). https://schunk.com/sg_en/homepage/adheso/. 3. Vedantu. (2020, July 3). Van der Waals forces - AFFECTING FACTORS. VEDANTU. https://www.vedantu.com/chemistry/van-der-waals-forces-affecting-factors.
Please contact us if you are interested to see demo of Meca500.


